Introduction
Freshwater ecosystems include all bodies of water that contain less than 1% salt concentration. These can include rivers, lakes, ponds, wetlands, and other aquatic environments. Freshwater ecosystems are incredibly diverse, and support a wide variety of plants and animals.
Types of Freshwater Ecosystems
Freshwater ecosystems can be divided into two main types: lentic (standing water) and lotic (flowing water) systems. Lentic systems include lakes, ponds, and wetlands, while lotic systems include rivers and streams. Each type of ecosystem has its own unique characteristics and supports a specific set of plant and animal species.
Flora
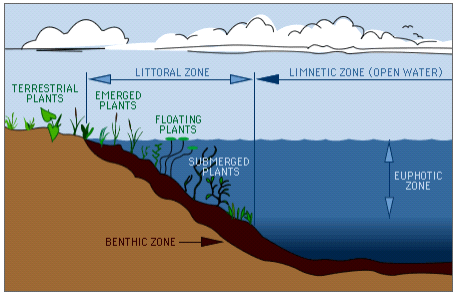
Plants in freshwater ecosystems are incredibly diverse, and can include submerged aquatic plants, emergent plants like cattails and bulrushes, and floating plants like water lilies. These plants provide food and habitat for a variety of aquatic organisms, and play an important role in maintaining the health of freshwater ecosystems.
Fauna
Freshwater ecosystems are home to a wide variety of animals, including fish, amphibians, reptiles, insects, and mammals. Some common freshwater animals include trout, bass, frogs, turtles, dragonflies, and beavers. These animals are adapted to life in or near water, and have unique features that help them survive in freshwater environments.
Human Impact
Human activities have had a significant impact on freshwater ecosystems. Pollution from agriculture, industry, and urban development can have a devastating impact on water quality, and can harm plants and animals that depend on clean water. Overfishing and the introduction of non-native species can also have a negative impact on freshwater ecosystems. Climate change is also a major threat to freshwater ecosystems, as rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can have a significant impact on the plants and animals that call these environments home.